STACK Implementation using Array with PUSH, POP, TRAVERSE Operations
Introduction
Stack is a simple data structure with a predefined capacity that allows adding and removing elements in a particular order i.e. Stack work on LIFO (Last in, First out) technique. Every time an element is added, it goes on the top of the stack, the only element that can be removed is the element that was at the top of the stack. The Stack falls in linear data structure. The stack was first proposed in 1946.
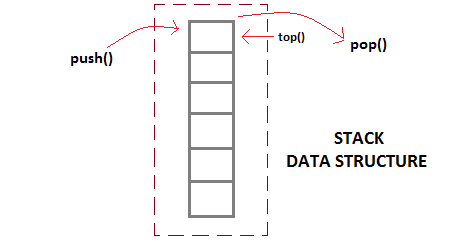
Example
In this example we will implement stack with the help of class and object, in this example stack will be implemented with following operations:
- Stack Initialization
- Push Operation
- Pop Operations
- Check Empty
- Check Full
- Stack Traversing to Display Stack Items
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#define SIZE 5
namespace std {}
using namespace std;
class STACK
{
private:
int num[SIZE];
int top;
public:
STACK();
int push(int);
int pop();
int isEmpty();
int isFull();
void displayItems();
};
STACK::STACK()
{
top=-1;
}
int STACK::isEmpty()
{
if(top==-1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int STACK::isFull()
{
if(top==(SIZE-1))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int STACK::push(int n)
{
if(isFull()){
return 0;
}
++top;
num [top]=n;
return n;
}
int STACK::pop()
{
int temp;
if(isEmpty())
return 0;
temp=num[top];
--top;
return temp;
}
void STACK::displayItems(){
int i;
cout<<"STACK is:";
for(i=(top);i>=0;i--)
cout<<num[i]<<"";
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
STACK stk;
int choice,n,temp;
do {
cout<<endl;
cout<<"0-Exit."<<endl;
cout<<"1-Push Item."<<endl;
cout<<"2-Pop Item."<<endl;
cout<<"3 - Display Items (Print STACK)."<<endl;
cout<<"Enter your choice: ";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice){
case 0: break;
case 1:
cout<<"Enter item to insert: ";
cin>>n;
temp=stk.push(n);
if(temp==0)
cout<<"STACK is FULL."<<endl;
else
cout<<temp<<" inserted."<<endl;
break;
case 2:
temp=stk.pop();
if(temp==0)
cout<<"STACK IS EMPTY."<<endl;
else
cout<<temp<<" is removed (popped)."<<endl;
break;
case 3:
stk.displayItems();
break;
default:
cout<<"An Invalid choice."<<endl;
}
}while(choice!=0);
return 0;
}Output
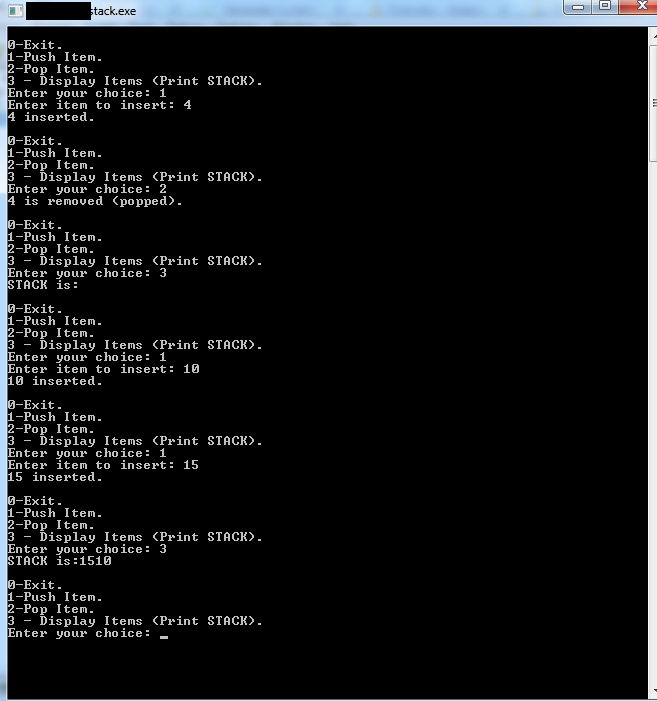
Conclusion
Hope it will help to understand the stack data strucure in C++.
0 Comments







